Understanding Mesopotamia Social Structure: A Deep Dive Into Ancient Civilization
The Mesopotamia social structure was a complex and hierarchical system that played a crucial role in shaping one of the world’s earliest civilizations. This ancient region, located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, witnessed the rise of various city-states and empires, each with its own distinct social organization. Understanding this social structure is essential for grasping the broader cultural, political, and economic dynamics of Mesopotamia.
In this article, we will explore the various layers of the Mesopotamian social hierarchy, the roles and responsibilities of different social classes, and how this structure influenced daily life in ancient Mesopotamia. We will also delve into key historical figures and events that shaped this civilization, providing a comprehensive overview of its social organization.
Join us as we unravel the intricacies of the Mesopotamia social structure, offering insights into how it functioned and its lasting impact on subsequent cultures and societies.
- Barron Trumps Girlfriend 2024 Who Is He Dating
- Who Is Karrueche Tran The Life And Career Of A Rising Star
Table of Contents
- Overview of Mesopotamia Social Structure
- Social Classes in Mesopotamia
- The Nobility Class
- The Role of Priests
- The Commoners
- The Slave Class
- Gender Roles in Mesopotamia
- Conclusion
Overview of Mesopotamia Social Structure
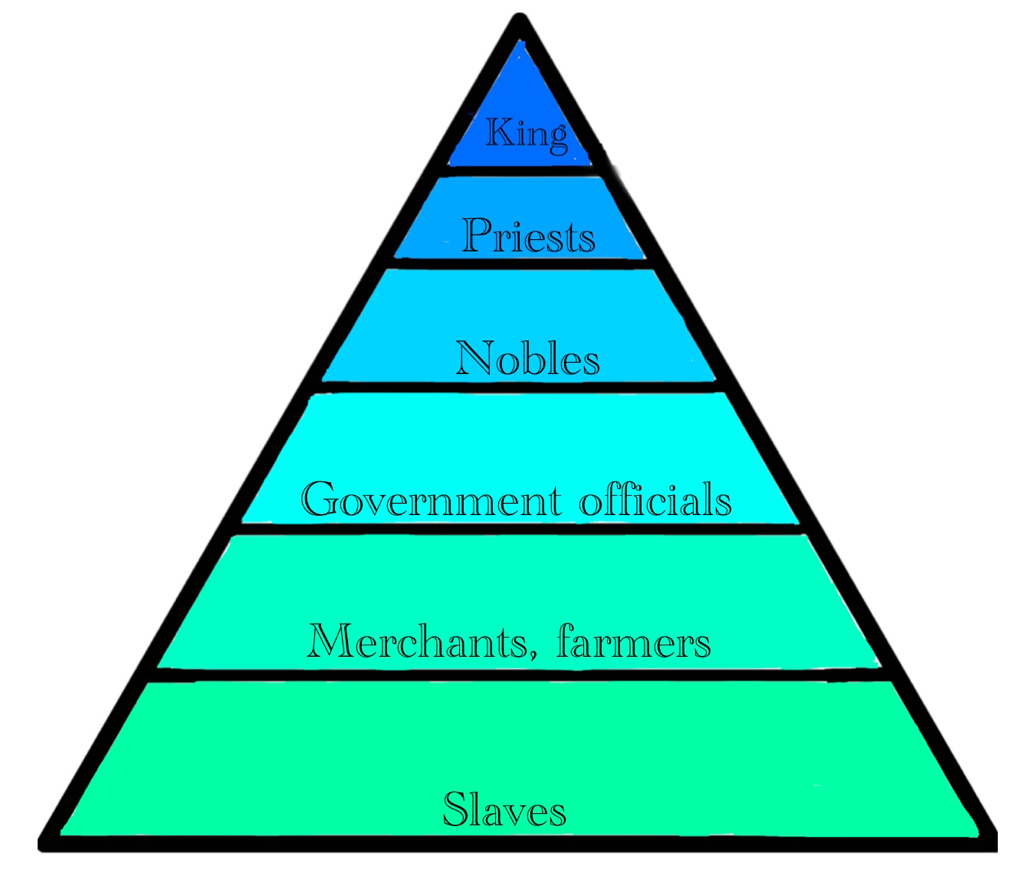
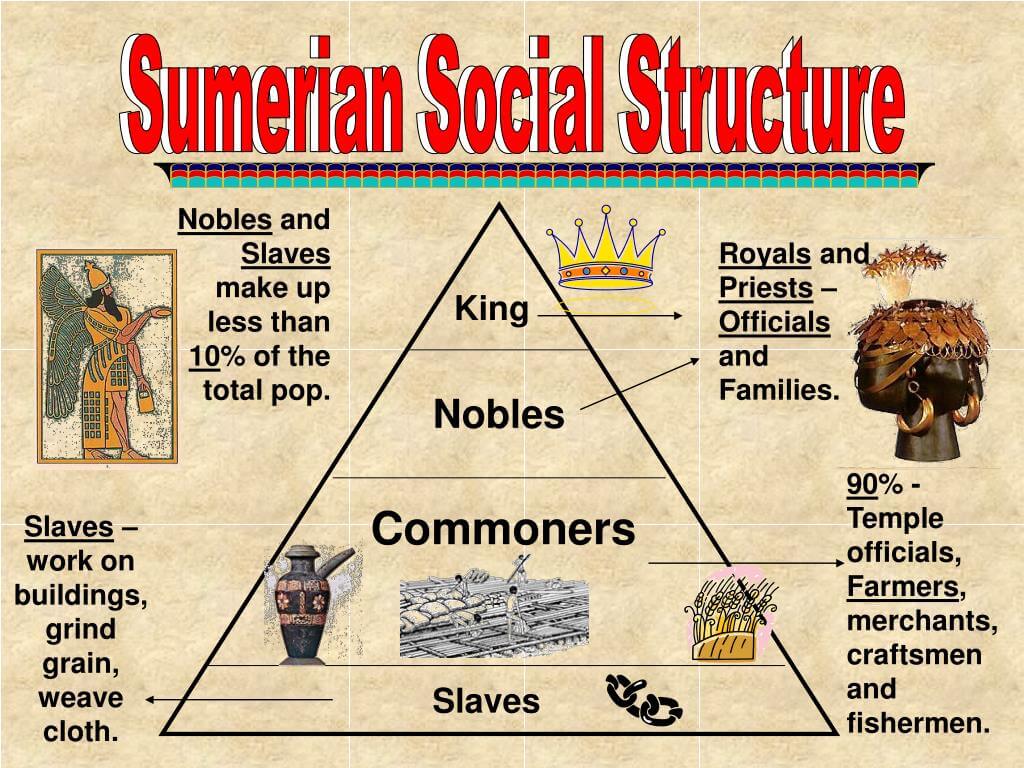
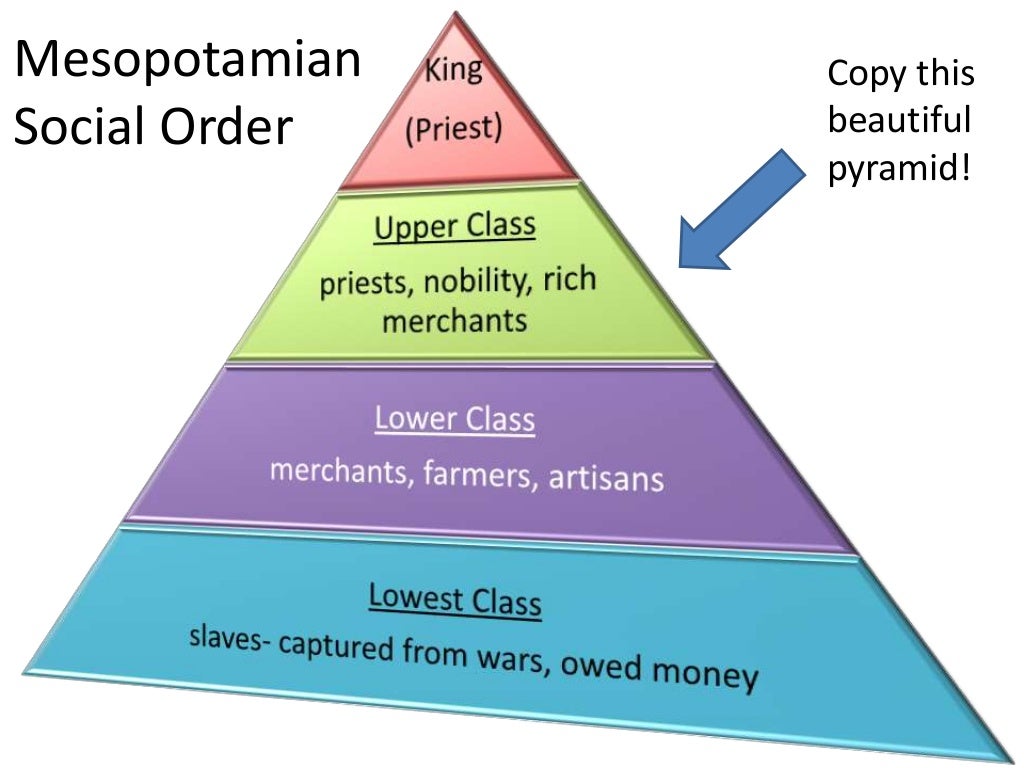
The social structure of Mesopotamia was characterized by a hierarchy that defined the roles and statuses of individuals within society. This structure was not only indicative of one’s wealth but also of one’s occupation and influence in the community. At the top of this hierarchy were the ruling classes, followed by priests, merchants, artisans, farmers, and slaves.
Each class had specific roles, responsibilities, and privileges that contributed to the functioning of Mesopotamian society. The intricate relationships among these classes fostered a dynamic social environment that facilitated trade, governance, and cultural development.
Social Classes in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamian society was divided into several distinct classes, each with unique characteristics. Understanding these classes provides a clearer picture of how Mesopotamians lived, worked, and interacted with one another. The main classes included:
- Travis Kelce Injury Update What You Need To Know
- Understanding Greg Gutfelds Health Insights Into His Illness
- The Nobility Class
- The Priest Class
- The Commoners
- The Slave Class
The Nobility Class
The nobility class in Mesopotamia consisted of kings, queens, and high-ranking officials who held significant power and influence. They were often landowners and enjoyed privileges that set them apart from the rest of society. Key features of the nobility class included:
- Wealth: Nobles possessed vast estates and resources.
- Political Power: They were involved in governance and decision-making processes.
- Social Status: Nobility enjoyed high social standing and respect from lower classes.
The Role of Priests
Priests held a prominent position in Mesopotamian society, serving as intermediaries between the gods and the people. Their responsibilities included conducting religious ceremonies, maintaining temples, and offering sacrifices. Important aspects of the priest class included:
- Religious Authority: Priests were seen as the guardians of religious knowledge and practices.
- Economic Influence: Many temples owned large tracts of land and employed numerous workers.
- Advisors to Rulers: Priests often advised kings on matters of state and religion.
The Commoners
The commoners made up the majority of the population and included farmers, laborers, artisans, and merchants. They played a vital role in the economy and everyday life of Mesopotamia. Key characteristics of commoners included:
- Economic Contribution: Commoners produced food, crafted goods, and engaged in trade.
- Social Mobility: Some commoners could rise to higher positions through hard work and skill.
- Community Life: They participated in local governance and cultural events.
The Slave Class
Slavery was a common practice in Mesopotamia, with slaves being used for various purposes, including labor, domestic work, and agricultural tasks. Important points regarding the slave class include:
- Sources of Slavery: Slaves were often prisoners of war, individuals in debt, or born into slavery.
- Living Conditions: While many slaves worked under harsh conditions, some were able to earn their freedom.
- Social Stigma: Slavery was generally viewed negatively, though it was an accepted part of the economic system.
Gender Roles in Mesopotamia
Gender roles in Mesopotamia were distinctly defined, with men typically occupying positions of power, while women were often relegated to domestic roles. However, women in Mesopotamia could own property, manage businesses, and hold religious positions. Key points include:
- Domestic Responsibilities: Women were primarily responsible for managing households and raising children.
- Economic Participation: Women could engage in trade and own businesses, particularly in textiles.
- Religious Roles: Some women served as priestesses and held significant religious authority.
Conclusion
In summary, the Mesopotamia social structure was an intricate system that defined the roles of various classes within society. From the powerful nobility and priests to the hardworking commoners and slaves, each group contributed to the civilization's development. Understanding this social hierarchy not only sheds light on the daily lives of ancient Mesopotamians but also provides insights into the cultural and religious practices that influenced their community.
We invite you to share your thoughts on this topic by leaving a comment below or exploring our other articles to learn more about ancient civilizations. Your engagement helps us create more valuable content for readers like you!
Thank you for reading, and we hope you found this exploration of the Mesopotamia social structure informative and enriching. We look forward to seeing you again soon!
- Exploring Yumieto A Comprehensive Guide To This Emerging Trend
- Understanding The Mls Playoff Structure A Comprehensive Guide
Social classes & Writing system Mesopotamia
Social Structure Of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia P.S.R.